With the rapid growth in spectrum demand due to the surge of new digital services enabled by 5G, spectrum management is becoming increasingly critical for ensuring consistent, affordable and equitable connectivity. About 11% of the world’s mobile connections are already on 5G today, and as networks advance that number will reach over 50% by 2030. In most cases 5G has used the mid-band 3.5 GHz launch range. As such, over time, the greatest demand will be placed on mid-band spectrum and the mobile industry is looking for ways as to how the mid-band demand can be met. In reality, countries are addressing this in only two ways:
- Maxing out the 3.5 GHz range (3.3-4.2 GHz) up to 4.2 GHz and even considering below 3.3 GHz
- By relying on adding more spectrum using 6 GHz
As such, the opening up of the 6GHz band is considered key to addressing the forthcoming challenges of reliable, high capacity, low latency and wide-area connectivity.
With the deployment of 5G networks, the future of the 6GHz band in the MENA region is paramount for supporting the national digital transformation goals and various other digital initiatives for consumers and industries. The 6GHz range is a mid-band that strikes a perfect balance between coverage and capacity, providing the perfect environment for 5G connectivity. Extending the bandwidth of 5G through the synchronization of the 6GHz spectrum will ensure more bandwidth and improve network performance. Additionally, the broad, close-link channels offered by the 6GHz range will reduce the need for network densification and make next-generation connectivity cost-effective for all.
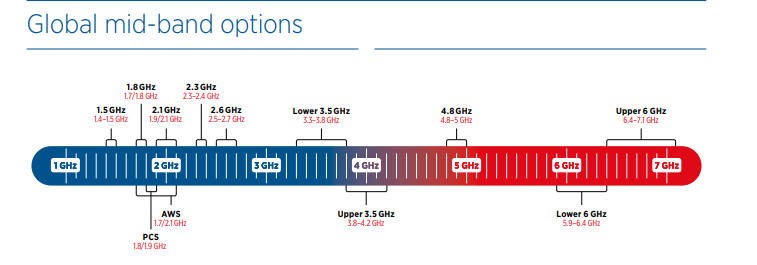
Source: GSMA
Mid-band demand drivers
Mobile data usage has been growing and will continue to do so into the future, requiring the availability of the mid-band spectrum. The 6GHz spectrum band comprises up to 1,200 MHz of new spectrum. Such a large amount of spectrum is a sweet spot for making new, fast and low-latency services such as driverless vehicles and on-demand video applications a reality.
Video consumption: Access to the mid-band spectrum is essential for the efficient relay of audio-visual communications, in-vehicle entertainment, streaming of high-definition video content, etc. Cisco reports that 82% of global internet traffic will come from either video streaming or video downloads in 2022 alone. Furthermore, add to that the demand mix of high-quality video for augmented or virtual reality (AR/VR).
Safer networks in smart cities: High-bandwidth hungry applications such as video surveillance, real-time text translation, video-based sensor networks and additional applications are an increasing part of public safety and emergency response systems in urban cities.
Industry 4.0 connectivity: Networks that can support Industry 4.0 applications such as 5G-based machine control, vehicle-to-network (V2N) services, robot connectivity, campus multimedia services and AR overlays for remote maintenance or construction support.
Fixed wireless access (FWA): FWA-based 5G networks can increase the level of competition among operators as well as access technologies, providing high-speed internet services to homes and businesses rather than traditional fiber optic cables. The Global mobile Suppliers Association (GSA) predicts that 5G FWA consumer premises equipment (CPE) shipments will reach 7.6 million in 2022.
Digital transformation: There are very few countries that have not embraced digital transformation as a way of developing their economies. Consequently, access to mid-band frequencies will be important to meet connectivity policies in an economically viable manner.
Furthermore, 6GHz also supports Fixed-Satellite Service (FSS) as well as Fixed Service (FS). It is expected that coexistence between IMT and fixed links will be possible through coordination.
As per GSMA research, the mid-band 5G spectrum will deliver more than $610 billion in global GDP in 2030, accounting for almost 65% of the overall socio-economic value generated by 5G.
State of 6GHz in MENA
In the Middle East, Etisalat UAE, branded as etisalat by e&, just announced the successful completion of its first trial of the 6GHz spectrum, accelerating the future of 5G and opening up a world of possibilities for next-generation technologies and economies of the future. The trial was conducted with Huawei Technologies which successfully completed several field tests on the 6GHz band, exploring the full speed and capabilities of 5G in the mid-band spectrum.
Last year, Saudi Arabia released the full 6GHz band to unlicensed use, opening up 1.2 GHz of new spectrum available to Wi-Fi. With this new expansion, Saudi Arabia became the first country in the Europe, Middle East and Africa regions to release the full 6GHz, securing the potential of leading the world in the availability of mid-band license-exempt spectrum.
Push for the mid-band
To achieve 5G’s potential, every country will require 2GHz of mid-band spectrum to meet demand by 2030, says GSMA. The industry body recommends governments around the world determine the most efficient use of the 6GHz spectrum and subsequently invest in the future of mobile deployment of 5G in the upper 6GHz band to maximize those socio-economic benefits delivered by 6GHz.
“5G development is gearing up globally; most of the countries have taken 5G in a strategic position to enable the national digitalization in the coming decade. It is highly recommended that governments implement favorable industry and spectrum policies to facilitate the evolution of 5G in the MENA region,” says Asmae Lachhab, Senior Marketing and Solution Manager, Huawei Northern Africa.
In June, the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) completed the standardization of the upper 6 GHz spectrum (U6G, 6425–7125 MHz) as an IMT licensed band for NR and as part of Release 17. 3GPP approval of the band’s RF specifications for both network and user equipment facilitates the development of products for this spectrum. This will be supported by IMT identification at the World Radiocommunication Conference 2023, and taking these steps will provide the necessary spectrum capacity to secure 5G innovation and growth.
“We have reached an important stage of the WRC-23 preparation. ITU-R working parties and task groups are completing the technical studies for each agenda item,” said Mario Mankiewicz, Director of Radiocommunication Bureau, ITU.
With WRC-23 approaching, positive engagement on mid-band solutions for International mobile telecommunication (IMT) will provide vital support to the harmonization of the spectrum, and hopefully give clear technical guidance for regulators. Coordinated regional decisions will lead to a WRC which enables the future of 5G and supports wider broadband take-up by increasing capacity and reducing costs.
The UAE and the Middle East are focused on embracing the digital transformation wave across various industries. As per Gartner, IT spending in the MENA region is forecast to total $173 billion in 2022, growing 1.2% from 2021. While worldwide IT spending is projected to total $4.5trln in 2022, an increase of 3% from 2021. With the rise of digital advancements such as the metaverse and other digital systems, the importance of future readiness, competitiveness, flexibility and digital alignment between projects and digital systems will become all the more critical and complex. Harnessing the capabilities of high-bandwidth supporting band such as 6GHz warrants unbiased priority.










